The banking sector, an integral part of the global economy, has always been a hub of various financial activities and services. At the forefront of this industry are bank tellers, key personnel who often serve as the first point of contact for customers. These professionals play a crucial role in daily banking operations, handling tasks such as cash transactions, account management, and customer service.
In an industry where precision and trust are paramount, understanding the compensation of these pivotal employees is essential. This article aims to shed light on the salaries of bank tellers in the United States, offering insights into what influences these wages and how they compare across different parameters. Whether you are considering a career as a bank teller or simply curious about the financial aspects of this role, we hope this Banks.org article provides you with an understand on how much bank tellers make.
What is a Bank Teller?
Definition and Primary Responsibilities
A bank teller is a financial service professional who manages a variety of transactions at banking institutions. Their responsibilities extend beyond handling cash; they are also tasked with processing checks, issuing savings bonds, taking loan payments, and providing account-related information to customers.
Key Skills and Qualifications Required
To excel in this role, a bank teller must possess a blend of skills including strong numerical ability, attention to detail, and excellent customer service skills. Generally, a high school diploma is sufficient for entry into this career, but additional qualifications like a bachelor’s degree in finance or related fields can enhance job prospects and salary potential.
How Much Bank Tellers Make in the United States
In 2024, understanding the financial compensation of bank tellers is pivotal for both individuals pursuing a career in banking and for financial institutions aiming to maintain competitive and fair salary structures. This comprehensive analysis delves into the various aspects of bank teller salaries, including hourly wages and annual earnings, drawing from multiple reliable sources to present an accurate picture of the current state of bank teller compensation.
Bank Teller Average Hourly Wage: $17/hour
- PayScale’s Insights (2023): According to PayScale, the median hourly pay for a bank teller as of 2023 was $15.18, with the potential to reach up to $18.87 for the top 90% earners. The range of hourly rates spanned from $12 to $19, with additional financial perks like bonuses ranging from $200 to $3,000, profit sharing between $233 to $4,000, and commissions from $97 to $5,000, culminating in a total pay scale that varied from $24,000 to $40,000 annually.
- Indeed’s Analysis (2024): According to Indeed, the average hourly wage for a teller was $17.08 as of early 2024, based on data collected from around 11,000 salaries. This figure provides a contemporary snapshot of the hourly compensation for tellers across the United States.
Bank Teller Average Annual Salary: $36,000/year
- Zippia’s Report (January 2024): Zippia reported an average annual salary of $32,043 for bank tellers. This figure represented the median, with entry-level salaries starting around $26,000 and extending up to $38,000 for the top 10% earners.
- AvgPay.com’s Data (2024): AvgPay.com listed the average annual salary for bank tellers in the United States as $35,737. The salary range was quite broad, with the lowest 10% earning around $28,063 and the highest 90% earning up to $49,648, highlighting the significant variance based on factors such as experience, location, and bank size.
The data from these diverse sources indicates that bank teller salaries in the United States exhibit a broad spectrum, influenced by various factors including geographical location, experience, and the specific policies of financial institutions. While hourly wages provide a baseline understanding of compensation, the total annual salary is impacted by additional benefits and incentives. This comprehensive analysis underscores the dynamic nature of bank teller salaries, reflecting the evolving landscape of the banking industry in 2024.
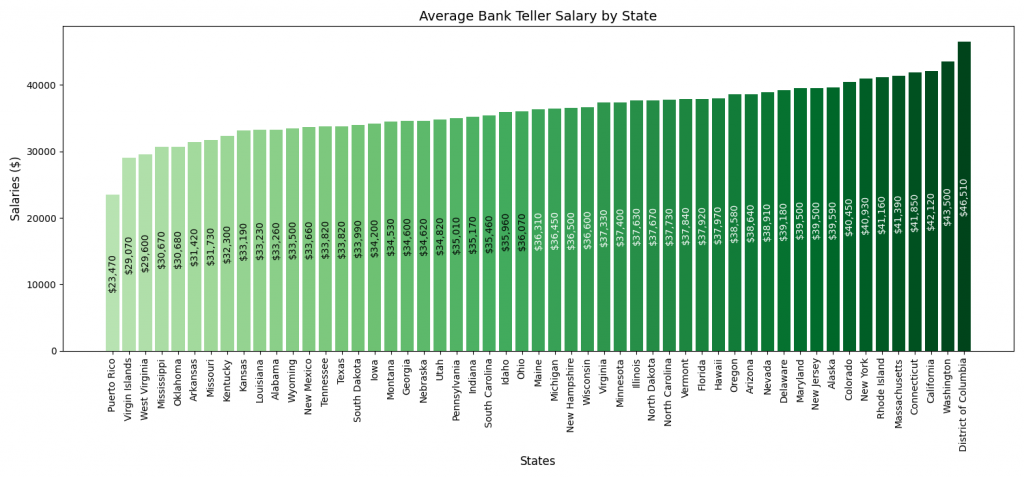
Salary Variations by Location
The salary of bank tellers in the United States varies significantly across different states. This variation is influenced by factors such as the cost of living, the state’s economic condition, and the demand for banking services. The below bar chart shows the latest Bureau of Labor Statistics data.
Top-Paying States
- Washington D.C. leads with the highest average salary for bank tellers at $46,510.
- California and Washington State follow closely, offering $42,120 and $43,500, respectively.
- Other states like Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Rhode Island also offer competitive salaries, ranging from $41,850 in Connecticut to $41,160 in Rhode Island.
Range of Salaries Across States
- The range of salaries across various states is quite broad, reflecting the diverse economic landscapes within the U.S.
- For instance, states such as Ohio, Minnesota, and Oregon have average salaries ranging from $36k to $38k.
- On the lower end of the spectrum, states like Texas, Oklahoma, Kentucky, and West Virginia have lower average salaries, with West Virginia being the lowest at $29,600.
- This disparity highlights the impact of regional economic factors and cost of living on bank teller salaries.
These salary variations underscore the importance of considering geographic location when evaluating bank teller positions. While some states offer significantly higher salaries, they might also be associated with higher living costs. You can view more salary data at Tellers : Occupational Outlook Handbook: : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (bls.gov).
Factors Influencing Bank Teller Salaries
Geographic Location
The salary of a bank teller can vary significantly based on geographic location. In general, tellers in urban areas or financial hubs tend to earn more than those in rural settings due to the higher cost of living and greater demand for banking services in these areas. Additionally, specific states or regions within the United States may offer higher average salaries due to local economic conditions and the concentration of banking institutions.
Experience and Education Level
Experience is another crucial factor influencing bank teller salaries. Entry-level tellers typically earn less than their more experienced counterparts. As tellers gain experience, they often see a gradual increase in their earning potential. Furthermore, education can play a role; while a high school diploma might suffice for entry-level positions, additional qualifications, such as a bachelor’s degree in finance or a related field, can lead to better job prospects and higher wages.
Size of the Bank or Financial Institution
The size and type of the financial institution also impact the salary of bank tellers. Larger banks with a more extensive national or international presence often offer higher salaries and a broader range of benefits compared to smaller, local banks. Moreover, credit unions and community banks might offer different compensation structures compared to large commercial banks.
Historical Trends in Bank Teller Salaries
Changes Over the Years
The banking industry has seen numerous changes over the decades, and these changes have influenced the salary trends of bank tellers. Historically, teller salaries have gradually increased, reflecting the rising cost of living and inflation. However, these increments have not always been consistent, with periods of economic downturn or banking industry disruptions impacting salary growth.
Impact of Economic Factors
Bank teller salaries are not immune to broader economic trends. Factors such as national economic health, inflation rates, and the state of the job market play a significant role in determining salaries. For instance, during economic booms, salaries might rise due to increased demand for banking services, while economic recessions could lead to wage stagnation or even reductions.
Part-Time vs Full-Time Bank Teller Salaries
Differences in Compensation
The distinction between part-time and full-time employment significantly affects the salaries of bank tellers. Part-time tellers generally earn an hourly wage and may not have access to the same level of benefits as full-time employees, such as health insurance and retirement plans. Full-time tellers, on the other hand, often receive a comprehensive benefits package in addition to their regular salary, which can substantially increase their total compensation.
Pros and Cons of Each Employment Type
Choosing between part-time and full-time work depends on individual circumstances and career goals. Part-time positions can offer flexibility and might be suitable for those balancing other commitments, like education or family. However, full-time positions typically offer more job security, higher income potential, and career advancement opportunities. It’s essential for individuals considering a career as a bank teller to weigh these factors based on their personal and professional needs.
Benefits and Perks for Bank Tellers
Health Insurance and Retirement Plans
One of the key benefits for full-time bank tellers is access to health insurance and retirement plans. These benefits are significant factors in the overall compensation package and can vary based on the employer. Larger banks typically offer more comprehensive health coverage and attractive retirement plan options, such as 401(k) matching.
Opportunities for Bonuses and Incentives
In addition to basic salaries, many banks provide performance-based bonuses and incentives to their tellers. These bonuses can be linked to personal performance, branch performance, or overall bank profitability. Such incentives not only boost income but also serve as motivation for tellers to excel in customer service and other key performance areas.
Career Advancement and Salary Growth
Pathways for Progression
Career advancement opportunities for bank tellers can significantly influence their salary growth over time. Tellers with strong performance records and additional qualifications often have pathways to move into higher roles, such as head teller, personal banker, or branch manager. Each upward step typically comes with an increase in salary, reflecting the greater responsibilities and skills required.
Impact of Additional Qualifications and Promotions on Salary
Pursuing additional qualifications, such as certifications in banking or finance, can lead to higher salaries and more advanced positions. Banks often encourage continuous learning and may even provide support for further education. Promotions to supervisory or specialized roles usually come with notable salary increments, acknowledging the added expertise and leadership.
Subsection: Navigating Career Advancement
Navigating the path to career advancement in banking requires strategic planning and proactive career management. Building a network within the industry, seeking mentorship, and continuously updating skills are crucial for tellers aspiring to climb the career ladder. Understanding the internal promotion policies of their institution and the broader industry trends can also aid tellers in making informed decisions about their career progression.
Negotiating Salaries as a Bank Teller
Tips for Negotiating Salary During the Hiring Process
When applying for a bank teller position, it’s important to be prepared to negotiate your salary. Research the average pay for tellers in your area and understand the range for the role. During negotiations, highlight your relevant skills, experiences, and any specialized knowledge you bring to the position. Remember, negotiation is not just about the base salary; consider discussing other forms of compensation like bonuses, benefits, and opportunities for advancement.
Understanding the Market Rate and Your Worth
Knowing the market rate for bank teller positions in your region and having a clear understanding of your worth are crucial. Consider factors such as your level of education, experience, and the specific demands of the bank you’re applying to. Be prepared to articulate how your skills and experiences align with the bank’s needs and justify your salary expectations accordingly.
Comparison with Similar Roles in the Financial Sector
To provide a comprehensive understanding of bank teller salaries within the broader financial sector, it is essential to compare their earnings with those in similar financial roles as of 2024. This comparison highlights the variations in compensation across different positions within the industry.
- Financial and Investment Analyst
- Average Salary: $103,020
- Role: Analyzes financial data and investment opportunities.
- Financial Manager
- Average Salary: $153,460
- Role: Oversees the financial health of an organization, including financial reporting and strategy.
- Actuary
- Average Salary: $125,300
- Role: Specializes in assessing financial risk using mathematics and statistics.
- Investment Banker
- Average Salary: $162,715
- Role: Assists in raising capital by issuing and selling securities and advising on financial transactions.
- Accountant
- Average Salary: $83,980
- Role: Manages financial records and ensures compliance with tax laws.
- Personal Financial Advisor
- Average Salary: $119,960
- Role: Provides financial advice to individuals on investment, tax, and retirement planning.
- Compliance Officer
- Average Salary: $75,810
- Role: Ensures that an organization adheres to legal standards and internal policies.
- Loan Officer
- Average Salary: $80,570
- Role: Evaluates, authorizes, or recommends approval of loan applications.
- Budget Analyst
- Average Salary: $84,240
- Role: Assists organizations in managing their finances by preparing and analyzing budgets.
This comparison shows that bank tellers, while playing a vital role in the banking sector, often earn less than professionals in many other finance-related roles. However, the bank teller position serves as an entry point into the financial industry, offering opportunities for career advancement and salary growth. The disparity in salaries underscores the varied responsibilities, required expertise, and educational backgrounds associated with different roles in the finance sector. For more bank teller comparisons, including their respective salary data, the BLS provides a detailed overview at Business and Financial Occupations – Occupational Outlook Handbook.
Bank Teller Salary FAQs
What is the starting salary for a bank teller in the United States?
The starting salary for a bank teller, often considered for entry-level positions (Bank Teller I), is around $32,030 annually. This figure can vary based on geographic location and the specific bank’s policies.
What is the average salary for a bank teller in the United States?
As of the most recent data, the average salary for a bank teller is $36,800 per year. This figure represents the mean annual wage for bank tellers across various states and financial institutions.
How does experience impact a bank teller’s salary?
Experience plays a significant role in determining a bank teller’s salary. As tellers gain more experience, their salary tends to increase. For example, a Bank Teller III, who typically has more experience and responsibilities, can earn an average of $39,400 annually.
Are there opportunities for bank tellers to receive bonuses or additional incentives?
Yes, many banks offer performance-based bonuses and incentives to bank tellers. These can include bonuses linked to personal or branch performance, profit sharing, and commissions.
What are the career advancement opportunities for bank tellers, and how do they affect salaries?
Bank tellers have various opportunities for career advancement, which can significantly impact their salaries. Advancement to roles like head teller, personal banker, or branch manager typically comes with an increase in salary. Additionally, pursuing further qualifications, such as certifications in banking or finance, can lead to higher-paying positions and more advanced roles within the banking sector. Career progression not only reflects in higher salaries but also in more complex responsibilities and a broader skill set.
What skills and qualifications are required to become a bank teller?
Bank tellers typically need strong numerical ability, attention to detail, and excellent customer service skills. A high school diploma is usually sufficient for entry-level positions, but additional qualifications like a bachelor’s degree in finance or related fields can lead to better job prospects and higher salaries.

Leave a Reply